Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. This burgeoning health issue has gained attention due to its rising prevalence worldwide. Understanding its causes, risks, and natural remedies is essential for anyone looking to improve their health. In this article, we will delve deeply into metabolic syndrome, offering insights and actionable advice.
What is Metabolic Syndrome?
Metabolic syndrome is not a single disease but a group of risk factors that occur together. These factors include:
- Abdominal obesity: Excess fat around the waist.
- Insulin resistance: Impaired ability of the body to use insulin.
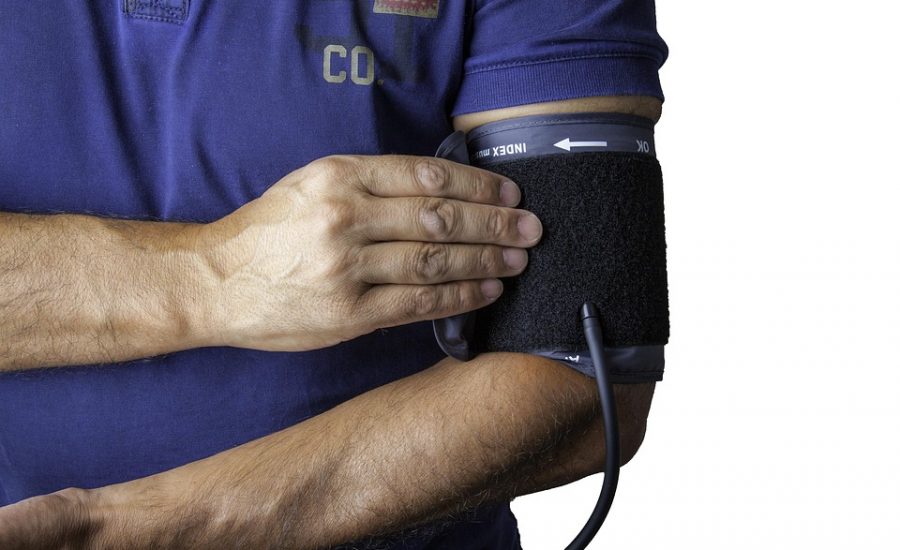
- High blood pressure: Elevated blood pressure levels.
- High blood sugar: Increased glucose levels in the blood.
- Abnormal cholesterol levels: Low HDL (good cholesterol) and high triglycerides.
Why It Matters
According to the CDC, approximately 34% of adults in the U.S. have metabolic syndrome. This alarming statistic signals the need for greater awareness and preventive measures. Combatting it can significantly reduce the risks of severe health complications.
Causes of Metabolic Syndrome
Identifying what leads to metabolic syndrome is crucial for prevention. Several factors contribute to its development:
1. Genetics
- Family history: A genetic predisposition can increase the likelihood of developing metabolic syndrome.
2. Lifestyle Factors
- Poor Diet: Diets high in sugar, refined carbs, and unhealthy fats contribute to obesity and insulin resistance.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyles reduce the body’s ability to maintain normal glucose levels.
3. Obesity
- Obesity, particularly central obesity (fat stored around the abdomen), is a significant risk factor.
4. Hormonal Changes
- Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and menopause can influence metabolic health.
5. Age and Gender
- Age increases the risk, and men are more likely to develop metabolic syndrome than pre-menopausal women.
Risks Associated with Metabolic Syndrome
Understanding the risks helps emphasize the urgency of managing metabolic syndrome. Common risks include:
1. Heart Disease
- Individuals with metabolic syndrome are twice as likely to have heart disease.
2. Stroke
- The combination of high blood pressure and poor lipid profiles increases stroke risk.
3. Type 2 Diabetes
- Insulin resistance directly leads to an increased likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
4. Liver Disease
- Fatty liver disease is often associated with metabolic syndrome, leading to liver damage.
5. Sleep Apnea
- Excess weight increases the risk of sleep apnea, which can exacerbate health issues.
Natural Remedies for Metabolic Syndrome
If you are looking for ways to combat metabolic syndrome naturally, there are several effective strategies. Here’s a list of remedies that can support your health journey:
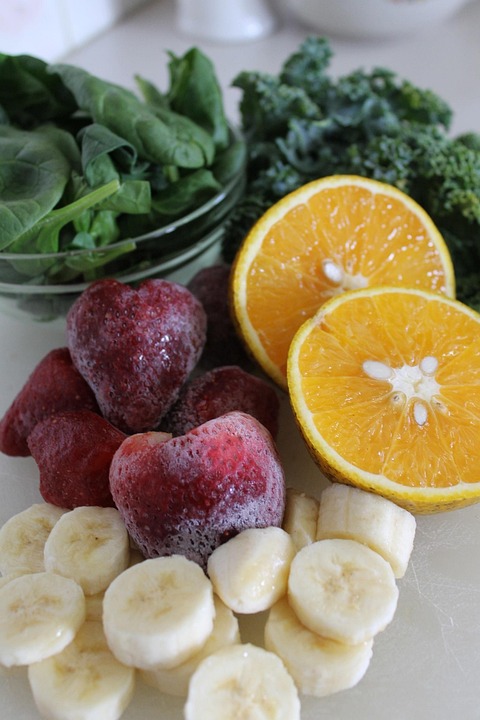
1. Healthy Eating
- Whole Grains: Include oats, quinoa, and brown rice to manage blood sugar levels.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a colorful plate to ensure nutrient diversity.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, nuts, and seeds.
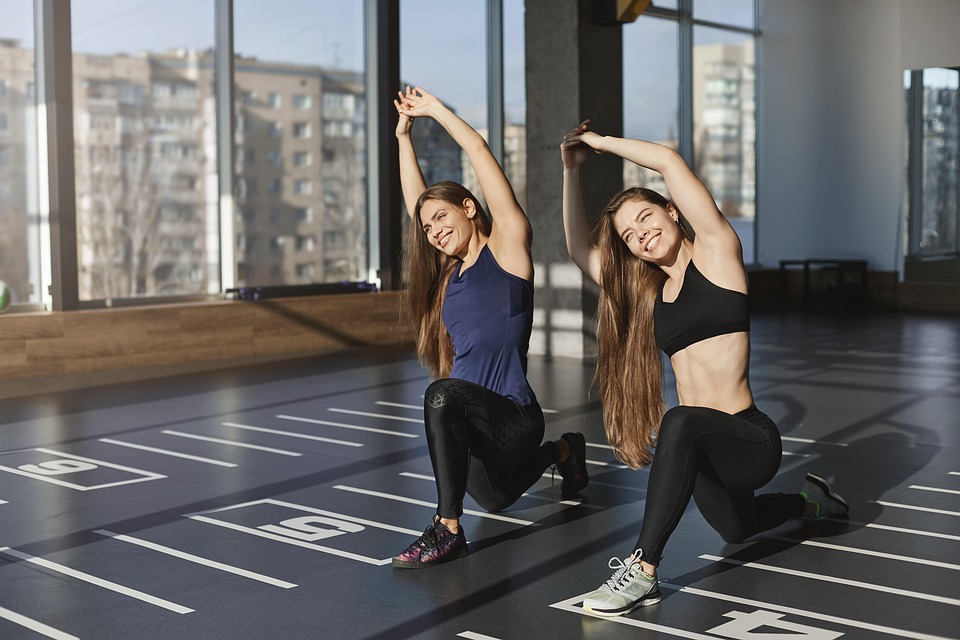
2. Regular Physical Activity
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Activities may include walking, cycling, swimming, or yoga.
3. Weight Management
- Losing even 5-10% of your body weight can significantly improve health outcomes.
4. Stress Management
- Practice mindfulness, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises to lower cortisol levels, which can contribute to weight gain.
5. Adequate Sleep
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support hormonal balance.
6. Hydration
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day. It helps with metabolic processes and can reduce cravings.
7. Supplements
- Consider omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, and fiber supplements after consulting a healthcare provider.
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect you have metabolic syndrome or exhibit symptoms such as increased abdominal fat, consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and intervention can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Diagnostic Criteria
Your doctor may use the following criteria to diagnose metabolic syndrome:
- Waist circumference: > 40 inches in men; > 35 inches in women.
- Blood pressure: ≥ 130/85 mm Hg.
- Fasting blood sugar: ≥ 100 mg/dL.
- Triglycerides: ≥ 150 mg/dL.
- HDL cholesterol: < 40 mg/dL in men; < 50 mg/dL in women.
Conclusion
Metabolic syndrome is a serious condition that requires immediate attention and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding its causes, recognizing associated risks, and implementing natural remedies can empower you to take control of your health. Whether you’re looking to prevent metabolic syndrome or manage it, these insights can lead to a healthier lifestyle. Remember, small changes can lead to substantial health benefits. Take that first step today toward a healthier, more vibrant life!







 Weight Loss, Unlocked.
Weight Loss, Unlocked.